The Metaverse is taking the world by storm and the second-largest economy, China, naturally shows no intention of missing out on the hype. However, given that the digital landscape in China has already shown its own characteristics, what would the making of the Metaverse be like in China? The Dao team spoke to Alvin Graylin, the China President at HTC, to understand how China would take on the race.

Mr. Alvin Graylin is the China President at HTC, leading all aspects of HTC’s business in the region. He is also currently Vice-Chairman of the Industry of Virtual Reality Alliance. Mr. Graylin has over 28 years of management experience in the tech industry, including 20 years in Greater China.
Mr. Graylin received his MS in computer science from MIT, MBA from MIT’s Sloan School, and BS in EE from the University of Washington, where he had specialized in VR and AI. Mr. Graylin is fluent in English, Mandarin, and Cantonese.
Could you please give us an overview of the Metaverse in China?
Metaverse is not something that is geographical. There isn’t a China Metaverse, a US Metaverse, a British Metaverse, etc. Also, the Metaverse should be not owned/controlled by any one company or person. At the end of the day, it’s the next evolution of the Internet and the Internet is an open global phenomenon, built on global infrastructure.
The Metaverse should be not owned/controlled by any one company or person. At the end of the day, it’s the next evolution of the Internet.
So essentially taking the internet that is right now mostly focused on video, photos, and texts and adding in 3D content and interfaces. Of course, all the videos, pictures, and texts will still be available, and you can still view them, with 2D or XR devices. But more and more of our attention will move from 2D to 3D content, and when the content moves to 3D. We will be going from websites and apps today to 3D worlds and 3D experiences in the Metaverse future.
Although I don’t think China is going to be significantly different in the user experience, there may be some small differences. I think because of government policies, kind of like what’s happening on the internet today, there are certain sites that may not be accessible or certain features not available [in China]. But in general, the ultimate Metaverse that happens in China will be very similar to the Metaverse that happens in the rest of the world.
How is the Metaverse different from current virtual reality technology?
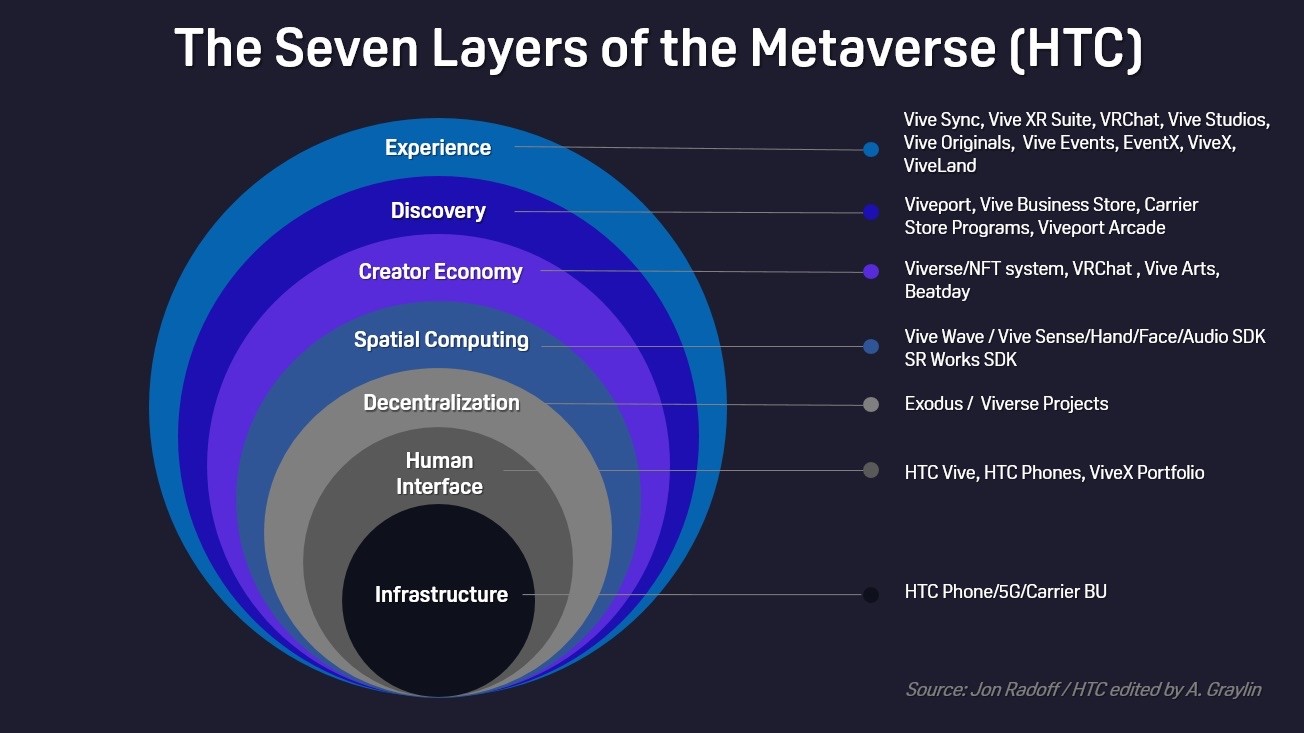
The Metaverse will be composed of many layers and Virtual Reality is one of the key layers. It’ll be the main interface technology we will use to access the future Metaverse. Just like right now, PCs and phones are the interface layer to the Internet. In the future, the interface layer to the Metaverse will be VR (Virtual Reality) devices and AR (Augmented Reality) devices. Inside the Metaverse, there will be a kind of network layer that powers everything – the servers and the communication networks. There will be a tools layer that helps people create content.
The Metaverse will be composed of many layers and Virtual Reality is one of the key layers.

There’ll be some kind of decentralisation layer that allows people to use their global identities, personal wallets, and custom avatars across various open worlds. Then you’ll do also the search and discovery layer so people can find the content that they want. Just like app stores, Google, and Baidu today. You’re going to have essentially a virtual world search type of system. And of course, there is going to be the content layer to all these experiences and worlds that people will make. So, a lot of the things that we see today on the internet, there will just be essentially equivalent versions of those things in the Metaverse.
How do you think the Metaverse would be developed in China?
I think just like any new technology disruption, most of the development will probably be led by private companies. But in China, the influence of the government is going to be stronger than in other parts of the world. So, as you were saying, things like new payment methods or currencies. In the rest of the world, there will likely be some kind of cryptocurrency that becomes the unifying payment model and an NFT system as the key asset validation model.
But in China, it will likely be the digital RMB as the major currency model, and then there will likely be some kind of a bridge that converts them for non-China worlds. And instead of decentralised NFTs, there may be a centralised system created by the Chinese government to serve those needed functions.
In China, it will likely be the digital RMB as the major currency model, and then there will likely be some kind of a bridge that converts them for non-China worlds.
So, I would assume that some of the companies that are major online internet technology leaders today will continue to be very relevant. But there will likely be a few companies that either are very small today or don’t exist today, that in 10 years will become the leaders in this new industry. I’m actually very optimistic about this new trend and the possibility of it, creating new experiences that really affect the world, and make our lives better.
How many main phases do you think there might be in developing Metaverse in China?
I think the Chinese government has done a decent job in recent decades in allowing new technologies to develop and reach wide adoption in the country fairly rapidly by not over regulating it too early. They let the market find the best means and then once it gets to a certain scale and it becomes a little bit clearer, what needs to be mandated or regulated before they start to act. I hope they will continue to follow this model so as not to delay this important innovation from reaching mass scale.

You’re right, that the Metaverse will not happen instantly and will develop over multiple phases. The first phase has already started in the creation of multiple walled gardens, which is allowing the market to naturally grow and allowing people to find new usage models, new business models, and new benefits that didn’t exist before. A number of sizable players will form and show good traction in the market.
Once it gets to a certain scale, I think then the government will start to come in and say okay, we believe that you should use this type of currency. We believe that you should use this type of an ID system, or we believe you should use this type of an asset identification system. Or whatever standards that they decide on that will allow for greater interoperability between all the key players.
The third phase will be when the Chinaverse then integrates with the global Metaverse.
The key to it working is that you have one Metaverse that everybody can go into. You don’t have the friction of signing in, putting in your ID, logging in, and putting money into separate accounts in every single world you visit. Because that’s how it works in the real world. So, the second phase is when the government will start to put in some of these mandates to enable a China-centric Metaverse (Chinaverse) that may even include some key allies markets.
Sometime after this, a more global standards Metaverse will likely start to form outside of the Chinese mandates. This may take some time, as getting 200 countries to agree to anything will not be easy. Other parts of the world will start to find their own solutions. As China’s going through the second phase, the rest of the world will be still trying to figure out and consolidating the first phase. By the time China figures out the second phase, then the world will probably start to get to the second phase of the regulations and may try to adopt some of the standards and learnings that have been created by China’s second phase.
The third phase will be when the Chinaverse then integrates with the global Metaverse. I think that’s when we finally have the full Metaverse experience with full interoperability globally seamlessly across all the open worlds that exist in it and we get the full benefit of a more efficient lifestyle and economy.
How do you think the Metaverse is going to impact the lives of ordinary people?
Honestly, I think almost all aspects of peoples’ lives will be impacted. We will spend more waking time in the Metaverse each day than in the physical world. Most of our interactions with other people and with information will be via the Metaverse. From school, to work, to play, within 10 years, most of these will happen in virtual worlds.
There’s a potential to create a new income/work model moving from working for a large company and getting a salary to becoming their own developer and content creator.
There will likely be significantly new business models that don’t exist today. As an example, there’s something called Play-to-Earn – essentially playing games to make money or to create virtual assets with real-world value. There are people who are not programmers who make little worlds and that they invite people to come to play their little virtual game and then they make money.
So, there’s a potential to create a new income/work model moving from working for a large company and getting a salary to becoming their own developer and content creator, even if they never learned how to program. I think there will be a significant portion of our population that will choose to work in the Metaverse versus having to commute to offices each day in the real world. As this new world develops, there are going to be more and more new types of business models that we haven’t even thought about.
One positive side effect is that if we won’t need to spend so much time commuting or time at the office/schools, so we’ll have more time for ourselves to spend on our hobbies, our health, and our loved ones.

How would the development of the Metaverse impact the environment?
Well, we spend a lot of our time driving around our city and traveling for work, and we buy a lot of things that we don’t really use, and a lot of people have multiple houses. There’s a lot of parking lots and offices that are only used less than half the time, and most cars are used less than 5% of the time of each day. Most of these wasted resources can be recovered and would in turn create a much less burden on our environment.
If you look at last year, during the period when most people were banned from flying, global carbon emissions actually went down by about 5% – I think that’s significant for just reducing one form of transportation. Now, transportation counts for about, 30 or 40% of total carbon emissions, so if we cut a lot of that down, I think that can have a big impact. Manufacturing and creating buildings make up another 30% [of the world’s total carbon emissions].
Most of these wasted resources can be recovered and would in turn create a much less burden on our environment.
So, as the world leaves their home less and travels less for business, we’re going to emit less carbon. Therefore, as we are digging less stuff out of the ground, we’re going to kill fewer trees, and these things will help the earth recover faster.
What do you think the hype of the Metaverse in China means to the company that is heavily dedicated to building virtual technology like HTC?
I think it’s a very positive thing that people are now recognising the value of what companies like us have been doing for many years. We’ve been focused consistently on building the technology, the infrastructure, the hardware, the tools to make the future Metaverse possible. A lot of people have not valued or didn’t know it.
But if you look at our stock price recently, it has just about tripled over the past two months. So clearly, the market now finally realises “companies like HTC are going to be more and more important in the Metaverse-first future”. This will allow us to have more resources to achieve our goals, have an easier time educating the market, and also make it easier for us to attract top talent.
Having that awareness is a good thing and especially for companies who are making a real difference.
In general, having that awareness is a good thing and especially for companies who are making a real difference, not just ones who really have nothing to do with the Metaverse but want to climb on the hype. [Those companies] that just put Metaverse in their press release to get attention may get a short-term pop, but the world and the stock market are pretty smart, so it won’t last.
Does HTC have any plans to get involved in the Metaverse If yes, how will it work?
We’ve been involved in building the basis for the Metaverse for over 7 years. In fact, in China, we’re the clear market leader for the VR industry and the whole Metaverse space. We’ve invested in over 100 start-ups to help support the ecosystem, created the tools that people are using today, most of the VR hardware companies in China who are in the industry are using our Wave runtime operating system and Viveport app store for their devices.
We are working with China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom to create better networks to allow for cloud VR in the 5G era. We’re helping set standards with the Chinese industry with the government so that they create better products that are healthy for users. In fact, just this year, we worked with China Mobile also to create a new global standard for mobile VR.
We share our technology and content with many companies that some may consider being our competitors so the entire industry can move faster.
So, it’s something that we’ve been doing, and we will continue to do this. We also operate the largest Open content store. I was talking about the different layers of the Metaverse [before], we have things in every single layer to enable the Metaverse to happen. These are things that we’re doing in China that no other companies doing. So, we are very focused on helping this industry make this new trend possible. We share our technology and content with many companies that some may consider being our competitors so the entire industry can move faster.
How do you think the application of the Metaverse will influence China’s economy?
I think China actually has an opportunity to leapfrog the world by adopting this technology faster than other markets. Just as China is striving to be the global leader in AI and or electric vehicles and solar power all these things, it has the opportunity to do so for the Metaverse as well.
If China can quickly achieve broad adoption of the Metaverse model, it will bring down a lot of costs that are unnecessary today. It will reduce traffic, be less dependent on imported resources, it will have more accurate tax collection, it will make the environment better, it will allow people to be more efficient/productive and enable the population to be more educated…essentially every factor of a vibrant economy.
Also, if you apply the digital RMB as the main payment model, then you’re also unifying the real and virtual economies and allowing for easier tax collection. I think China actually well-positioned to be the first country in the world to have a near-full Metaverse experience for its citizens.
I think China actually well-positioned to be the first country in the world to have a near-full Metaverse experience for its citizens.
Whereas the rest of the world will likely take much longer because they need to get 200 countries to agree to common standards, to agree on currencies and policies, and getting all of these companies to apply those common policies, which we know takes a long time.
But in a more government-managed market like China, the government can say this will be the standard. And the companies operating in the country will need to uphold the standards. That can happen very quickly. So, it’s a real opportunity for China to support some local champions, set some reasonable standards/policies, and leverage the benefits of this new operating model by promoting the virtual economy to show clear global leadership.
Read more:









